
“We have to build our half of the bridge, no matter who or where we happen to be.” – Colm McCann
Summary: Learning and pedagogical relationships are transformed when we engage with students in open online spaces or networked publics. These can become ‘third spaces’ of learning, beyond the binary of informal and formal learning. Once a closed classroom (physical or online) becomes open to the world, assessment options multiply, with many more opportunities for student choice, voice and creativity, and of course, feedback. [Slides] [Audio interview]
xx
This post summarises my talk at the eAssessment Scotland 2013 conference, “Assessment in Open Spaces”. I had planned to finish and publish this post last Friday, to mark the final day of the conference. However, hearing the sad news of Seamus Heaney’s death halted my progress and I wrote about Seamus instead. Today I return to eAssessment.
The eAssessment Scotland conference is a completely free, 2-week event which is open, distributed and accessible. The one-day conference at the University of Dundee on August 23rd was sandwiched between two weeks of online activity. Like the day conference, the online programme included keynotes and workshops, as well as numerous conversations on Radio EDUtalk. The conference, organised by David Walker, Kenji Lamb and others, is a unique opportunity for educators across many sectors — primary, secondary, third-level, community, commercial and government — to engage in discussions about learning and assessment.
I was one of three keynote speakers at the day conference, along with the wonderful Helen Keegan, a great friend and inspiration, and Fiona Leteney, whom I had the pleasure of meeting for the first time. I was invited to speak about Assessment in Open Spaces, but my presentation looked broadly at learning, teaching and assessment in open online spaces — and the imperative of doing this.
[slideshare id=25503738&style=border: 1px solid #CCC; border-width: 1px 1px 0; margin-bottom: 5px;&sc=no]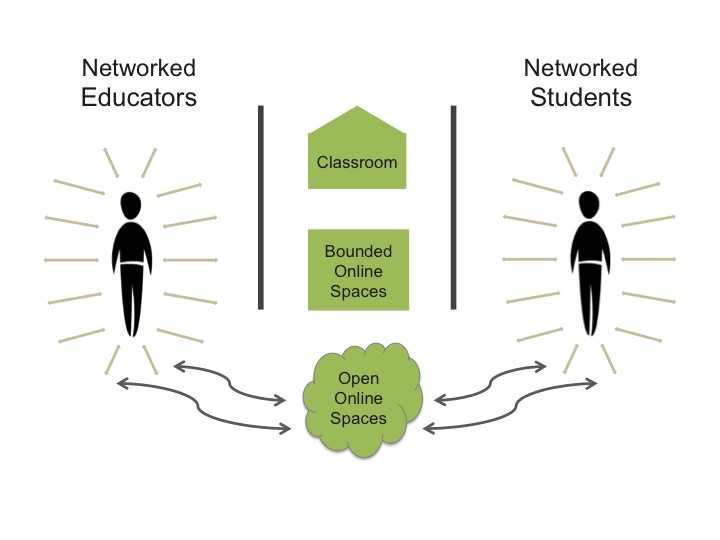 When we meet in physical classrooms and bounded online spaces, we learn and relate to one another but we cannot simultaneously learn with and from our networks, nor can we share what we are learning in the classroom (physical or virtual) with our networks. However, when we encounter one another in open online spaces, or Networked Publics as defined by danah boyd, we can interact and learn with our networks — communicating with one another, sharing our ideas and our work. And of course, we can share our Personal Learning Networks (PLNs) themselves. Open online spaces can become what Kris Gutiérrez, et al, call “Third Spaces” of learning; not formal learning space, not informal learning space, but a combined space. I find this concept of a “third space” very helpful in thinking about the possibilities of open online spaces for students and educators.
When we meet in physical classrooms and bounded online spaces, we learn and relate to one another but we cannot simultaneously learn with and from our networks, nor can we share what we are learning in the classroom (physical or virtual) with our networks. However, when we encounter one another in open online spaces, or Networked Publics as defined by danah boyd, we can interact and learn with our networks — communicating with one another, sharing our ideas and our work. And of course, we can share our Personal Learning Networks (PLNs) themselves. Open online spaces can become what Kris Gutiérrez, et al, call “Third Spaces” of learning; not formal learning space, not informal learning space, but a combined space. I find this concept of a “third space” very helpful in thinking about the possibilities of open online spaces for students and educators.The affordances of open online spaces for learning are many. Learners can establish new connections, within and beyond the classroom, based on their interests & passions. Learners can connect, share and work with others across the boundaries of institution, education sector, geography, time zone, culture and power level. And learners can build Personal Learning Networks which will serve them long after individual modules, courses and even programmes are finished. By engaging together in open online spaces we encourage and support students as they engage in participatory culture (see Henry Jenkins).
In my presentation I shared several examples of learning and assessment in open spaces at different levels of education — primary, secondary and third-level.
In the 2nd year Professional Skills module which I teach, in a BSc Computing and IT programme, students develop their research, writing and social media skills. We use open tools and open practices in many ways:
- We use Twitter (@CT231 and #ct231) to engage in conversations with people beyond our module, e.g. authors we are reading, other students, other educators, etc.
- Students give Ignite presentations in class on topics of their own choice. Their presentations are shared in a CT231 Student Showcase using Scoop.it; some presentation videos are also shared using Bambuser. Both enable communication to and feedback from people outside of our class.
- We participated in the #icollab project in 2013, joining students from 4 other institutions (Salford, Berlin, Barcelona, Auckland NZ) to share student-created media, peer-to-peer. Students from Salford and Auckland used Galway (CT231) students’ presentations to develop their own ideas and presentations; the process will continue in 2014 with Galway students building on the work of other #icollab students.
- Students openly shared their final Digital Media Projects, using Twitter and other social media to spread the word and invite feedback.
In terms of assessment in these open online spaces, students collectively created the rubrics for assessing their presentations and digital media projects. But that was not the whole story. Through engaging in open practices throughout the term, we became a learning community that was not confined to one classroom or one online space. The classroom walls thinned progressively as the term progressed, so that we truly became nodes in a broader network — sharing work openly, engaging in discussion, inviting and giving feedback. The main assessments for the module — the presentation and digital media project — were opportunities for students to chose their own topics, media, tools and ways of working (individual or team), to express their own authentic voices, and to share, engage and learn beyond the bounds of our classroom.
I discussed many of these ideas further in Radio EDUtalk conversations connected with the conference: with Karl Leydecker and John Johnston immediately after the keynote, and in a more wide-ranging discussion with Kenji Lamb, John Johnston and David Noble one week later. There are many fascinating conversations from conference participants on the Radio EDUtalk website, all collected under the #easc13 hashtag — well worth checking out.
Photo: Dundee Railway Bridge, CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 Tim Haynes
As usual, you have your hands on most intriguing and important work. Thanks for sharing this. As you know from our on-going conversations, this is an area of great interest to me as well. Looking forward to sharing more.
Many thanks, Jeff. Glad to be learning and heading down this road with other educators like yourself — teachers/educators/facilitators willing to relinquish control, embrace openness, and truly be learners alongside our students. Thanks 🙂